Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What is Thoracic Outlet?
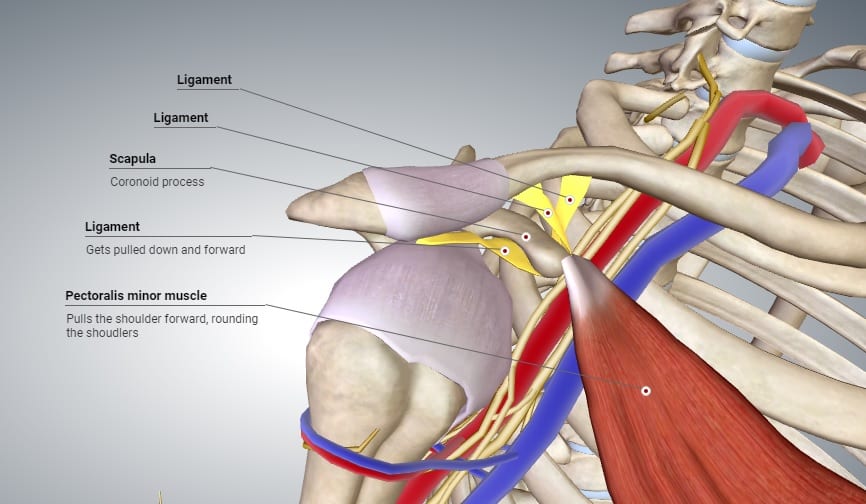
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a condition caused by compression of the nerves and bloods vessels as they exit the chest to supply the arm. This triangular region, bordered by the neck muscles, first rib and clavicle is referred to as the thoracic outlet. The symptoms caused by pressure in this specific region is referred to as Thoracic Outlet Syndrome.
What are the Causes?
There are three main types:Neurogenic,Venous, and Arterial.Neurogenic is the most common and presents with pain, weakness, and occasionally muscle wasting. Venous results in swelling, pain, and discoloration of the arm. Arterial results in pain, coldness, and altered blood flow.
What are the Risk Factors?
- - Congenital: developmental abnormalities around the vessels and nerves
- - Post-Traumatic: history of trauma to the area (e.g. clavicle fracture, whiplash, shoulder)
- - Functional: Repetitive lifting of the arm above the head (e.g. painter, swimmer)
- - Sex: Female > Male
- - Other: Less commonly other conditions (e.g. tumours)
Any condition that causes encroachment of the space for the nerves and vessels at the thoracic outlet can lead to thoracic outlet syndrome, including poor posture.
What are the Symptoms?
TOS symptoms depend of the region of compression. Nerve pain is the most common presentation and occurs predominantly in women aged 20-40years. Swelling and pain from deep vein thrombosis (DVT) are the most common symptoms of venous compression. Those with arterial symptoms present with pain especially during exercise or cold, pale fingers. Arterial aneurysms may be formed by compression on the vessel.
How can it be Identified?
Investigations can include nerve tests, such as Electromyography (EMG) and plain X-ray of the region. MRI is of limited value except when a tumour is suspected. The use of ultrasound in different arm positions can show problems in flow or an aneurysm caused by pressure in the shoulder.
What is the Treatment?
SURGICAL:Open surgical treatment to free the space and release the pressure on the nerves, artery or vein is the treatment of choice. The blood vessel can also be repaired at the same time
MEDICAL:Muscle injection also plays a role as a therapeutic tool in patients with nerve compression. Trauma patients who receive this treatment, particularly those treated soon after onset of symptoms, experience better results.
REHABILITATION:Despite the high rate of success with minimal complications associated with surgery, other options such as physical therapy, modifications to daily activities and medications are all options in treatment.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome remains a challenging entity to diagnose but treatment outcomes can be very successful and long-lasting given the correct patient selection.
Source: https://circulationhealth.com.au/thoracic-outlet-syndrome/